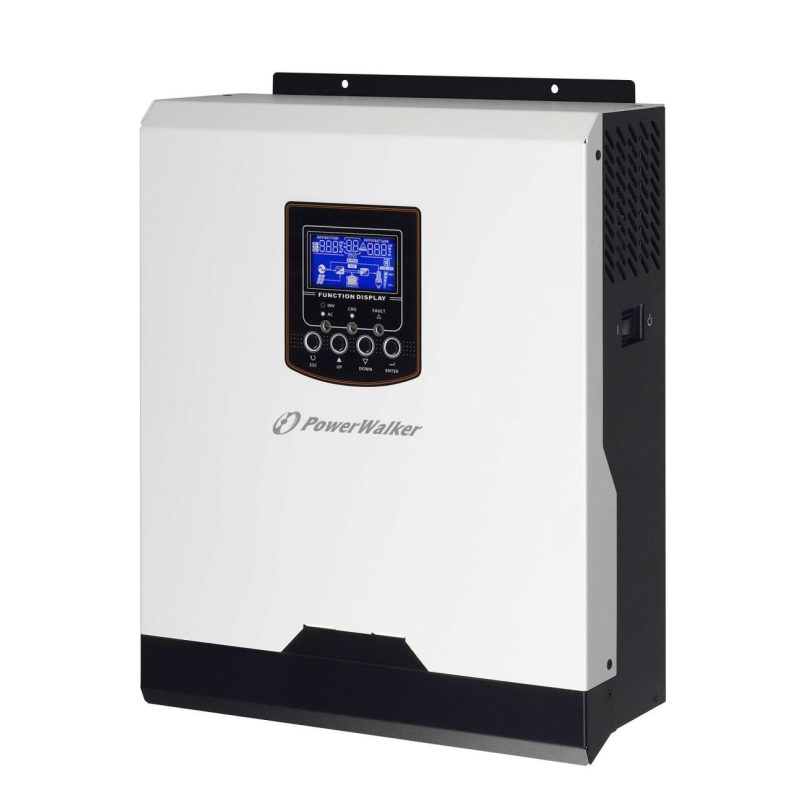
Inverters are commonly used in various applications where AC power is required, such as in homes, businesses, and renewable energy systems like solar photovoltaic (PV) installations.
Inverters work by utilizing electronic components such as transistors, capacitors, and diodes to switch the DC input into a high-frequency AC waveform. This AC waveform produced by the inverter is similar to the electricity supplied by utility grids.
There are different types of inverters available, including:
-
Stand-alone inverters: These inverters are used in off-grid systems where there is no access to the utility grid. They are often used in remote locations or for backup power systems.
-
Grid-tied inverters: These inverters are designed to synchronize with the utility grid. They convert DC power from sources such as solar panels or wind turbines into AC power that can be fed directly into the grid or used to power local loads.
-
Hybrid inverters: These inverters combine the features of stand-alone and grid-tied inverters. They can operate in grid-tied mode, off-grid mode, or both, making them suitable for applications with intermittent grid access or where backup power is required.
In addition to converting DC to AC power, some inverters also offer advanced features such as maximum power point tracking (MPPT) for optimizing the output of solar panels, grid stabilization functions, and communication interfaces for remote monitoring and control.
Overall, inverters play a crucial role in modern electrical systems by enabling the efficient and reliable conversion of power between DC and AC sources, facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources, and ensuring a stable supply of electricity for various applications.















There are no reviews yet.